Linux is the most used operating system. Linux is a free & open-source operating system, we can easily change anything on Linux. And Linux operating system provides a most powerful command-line interface. All Most-Used Commands On Linux run in the terminal. The terminal is provided by Linux operating system. All Linux commands are case-sensitive. We can do some basic tasks like creating files, deleting files, moving a file, etc.
Most-Used Linux Commands
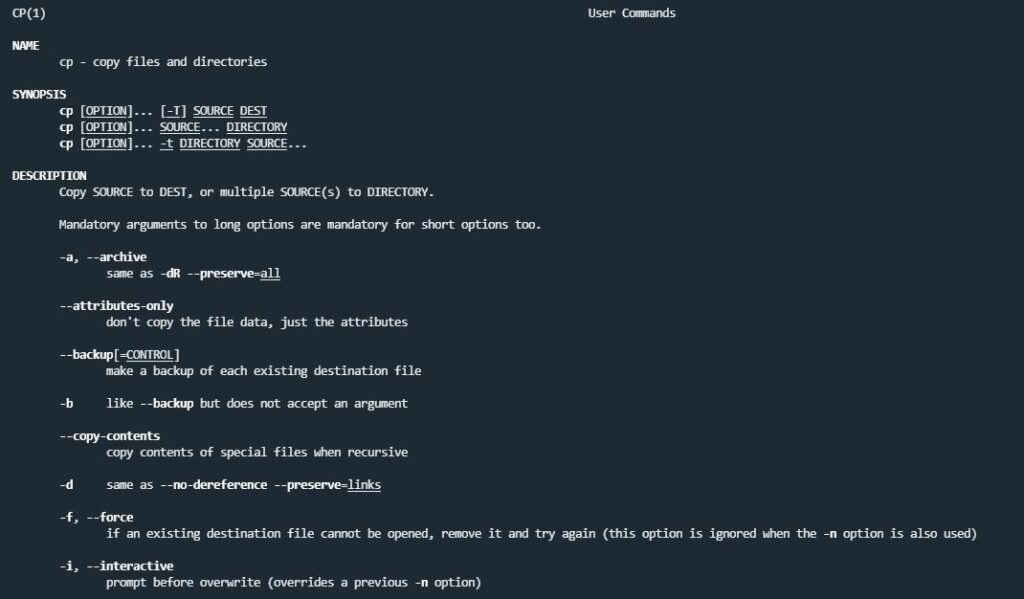
man Command
man command displays the manual page of any command. Using the man command, you can know what a particular command works.
man cp
Read Also: How to Install PostgreSQL on CentOS 7
ls Command
ls
ls is a firstly used command by every user in the Linux terminal. This command helps to show the list of directories & contents of the current directory.

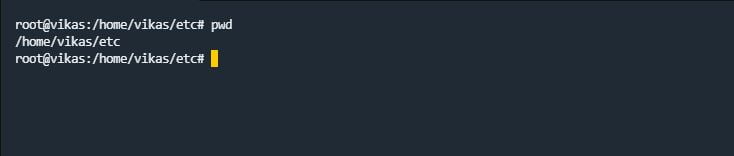
pwd Command
pwd command stands for “print working directory”. This command gives a path to the working directory.
pwd
cd Command
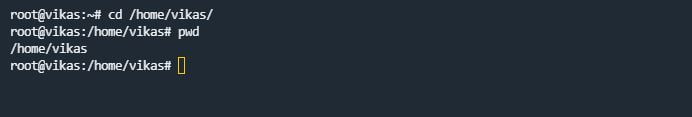
cd command stands for “change directory”. The cd command is used for changing the directory, which means we can switch from our current working directory to another directory with the help of the cd command.
For example:- If you are in your Linux servers /home/ directory and You want to go to another directory, then we will use this command like this.
cd /home/directory_name
mv Command
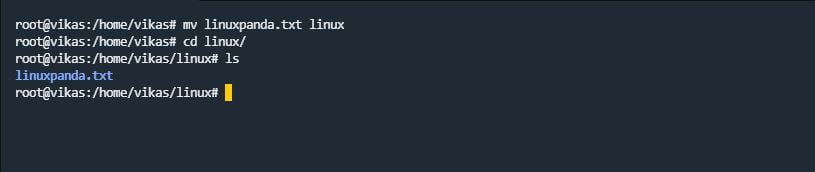
mv command stands for “move”. mv command is used to move the directories & files from one location to another location in our Linux system and we can also rename the files and directories using the mv command.
mv source_file destination_folder
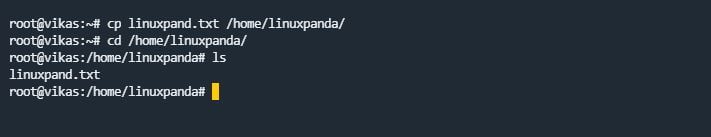
cp Command
cp command stands for “copy”. cp command is used to copy a file & directory from one location to another location in our Linux system.
cp file.txt destination_path
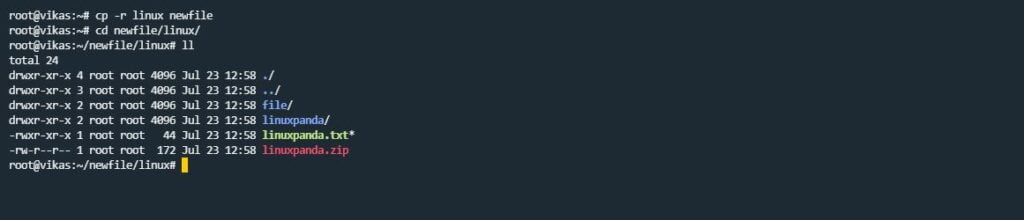
If you want to copy the directory with their files and subdirectories. You can use the “-r” (recursive) argument option.
cp -r file.txt destination_path
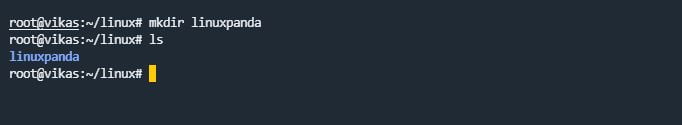
mkdir Command
mkdir command stands for “make directory”. mkdir command is used to create a new directory in the Linux system.
mkdir directory_name
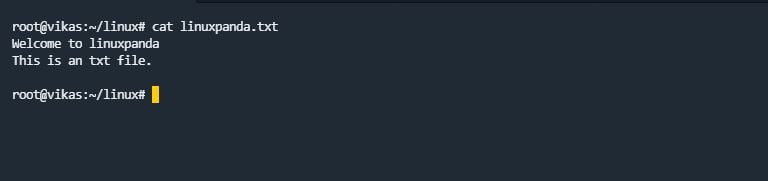
cat Command
cat command stands for “concatenate”. The cat command is used to display the content of the file. By using the cat command, we can see the contents of files without opening a file.
cat file_name
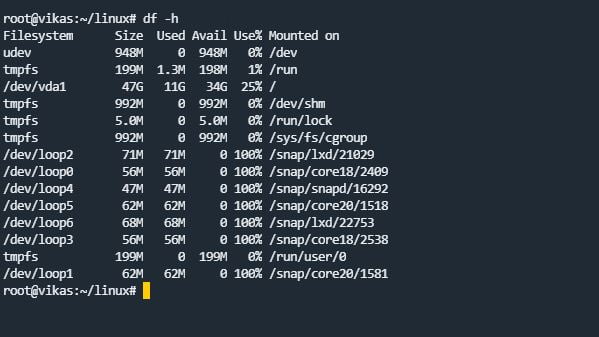
df Command
If you want to know the Disk space of our Linux system, we can use the df command. By default, disk space is shown in Kilobytes (KB). If you want to see the disk space in the human-readable form, then you can use the “-h” argument.
df -h
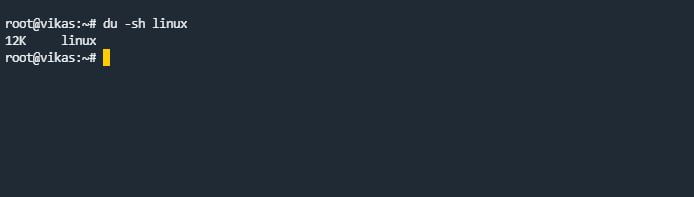
du Command
du command stands for “Disk Usage”. The du command is used to track the files and directories. That which files & directories are consuming an amount of space on disk.
If we want to see the particular directory and file usage, we can use the “-sh” argument. Using this display the size of the directory & file in human-readable form.
du -sh file_name
Read Also: Setup OpenVPN client for Windows
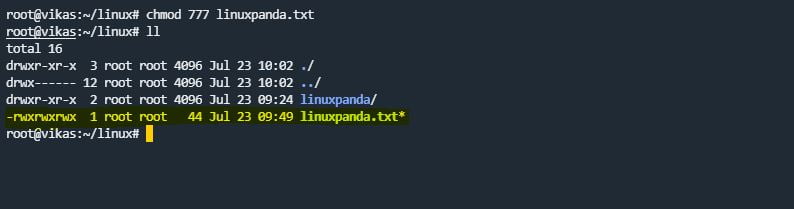
chmod Commands
chmod command stands for “change mode (Permissions)”. Using the chmod command, you can change the permissions of a file and directories. Permissions are like read “-r”, write “-w”, execute “-x”.
chmod 777 file_name
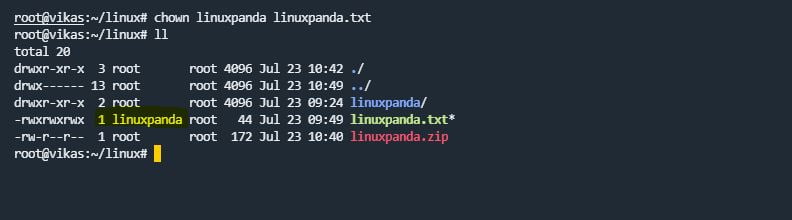
chown
chown command stands for “change ownership”. Ownership means you can change the owner/user of a particular file and directory. For example, our file name is “linuxpanda.txt” and the default owner of this file is “root” if you want to change the owner of the file to a “Linux” user use the chown command.
chown user_name file_name
chgrp Command
chgrp command stands for “change group ownership”. The chgrp command is used to change the ownership only for the particular groups. Group ownership means you can change the owner of a particular group of files and directories.
chgrp group_owner file_name
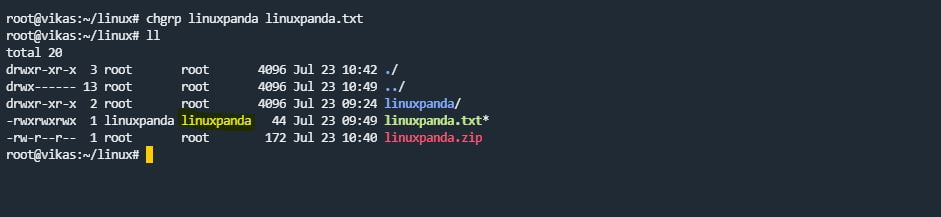
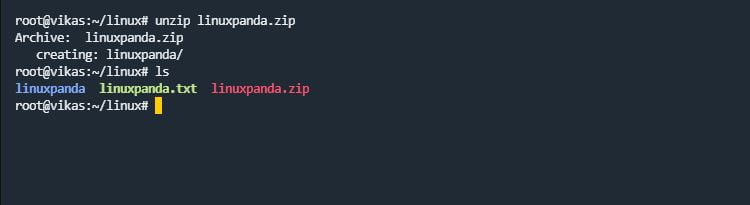
zip/unzip
zip command is used to create a zip file. Using the zip command, you can compress the file and directory. unzip command is used to extract the zip files.
zip newzipfile_name.zip file.txt
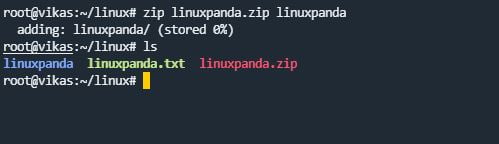
unzip zip_filename
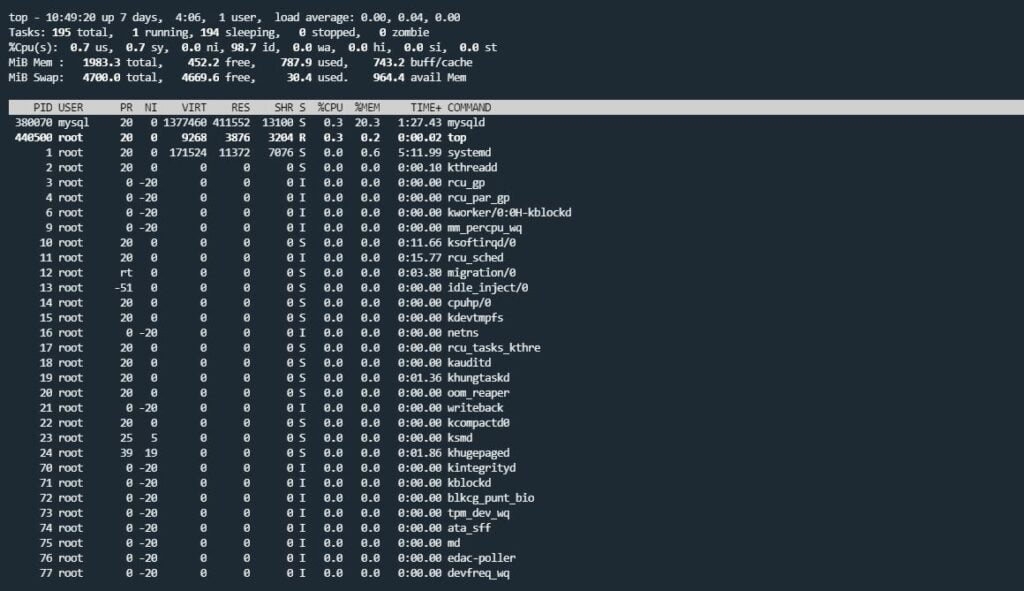
top Command
The top command is used to show the list of a running process and how much load or CPU is being used.
top
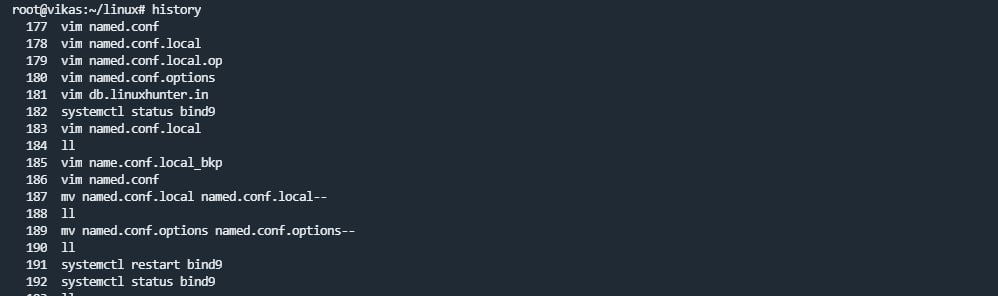
history Command
history command displays a list of all the commands that you are used in the past.
history
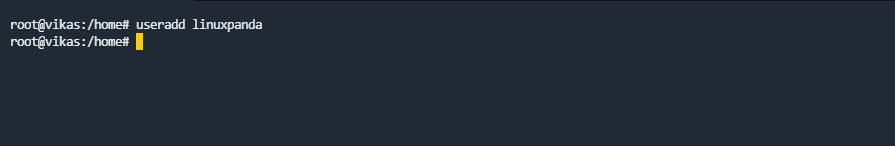
adduser Command
adduser command is used to create a new user in the Linux server. Also, you can use the useradd command for creating a new user on the Linux server.
useradd newuser_name
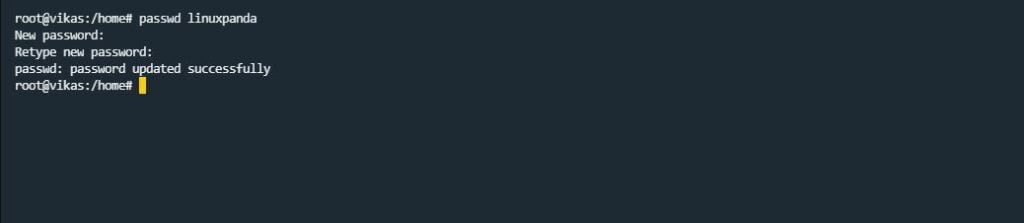
passwd Command
passwd command is used to set and change the user account password, And access the user account with a new password in our terminal.
passwd user_name
apt Command
apt command stands for “Advanced Packaging Tool”. It is the most used package manager for Ubuntu. apt is used for installing and removing the services and packages on our Linux server.
apt install package_name

clear Command
clear command is used to clear the terminal screen. Using the clear command, you can clear all previous commands and provide a fresh terminal window.
Also, you can use Ctrl+L to clear the terminal window.
clear
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned about the most-used Linux command and how to use the commands on Linux. We can use this tutorial for any Linux operating system like CentOS, Ubuntu, etc.
If you guys have any queries related to this tutorial, then let me know in the comments section.
















Leave a Reply